A microcontroller is a small, low-cost microcomputer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip, whereas a microprocessor is a form of computer processor in which both the data processing logic and control are incorporated on a single integrated circuit or small number of integrated circuits.
Through a microprocessor unit (MOU) and a few peripherals, it manages specific areas of an electronic system.
A microcontroller is a single chip that integrates memory, I/O, and a CPU, while a microprocessor is just a single CPU. Whereas an embedded system uses a microcontroller, personal computers employ microprocessors.
Microcontrollers employ internal controlling buses, but microprocessors use external buses to interface with RAM, ROM, and other peripherals.
Microprocessor vs Microcontroller: Selecting a suitable device on which to base the new design can be intimidating. The need to make the proper equilibrium of price, performance and power utilization has numerous implications.
In the first place, there will be prompt technology contemplations for the design you can embark on.
However, suppose a Microcontroller (MCU) or Microprocessor (MPU) becomes the basis of a platform approach. In that case, the decision can have long-lasting consequences.
At this point, the difference between microprocessors and microcontrollers becomes a critical point of debate.
Furthermore, it is reasonably challenging to spot the difference between microprocessor and microcontroller, as these two terms are the soul and core of programmable electronics.
Let this confusion go well and now for forever.
Here is all that you really want to have some familiarity with about these two core components, so buckle up your grey cells and let the learning begin on Logic Fruit Technologies.
What is a Microprocessor?
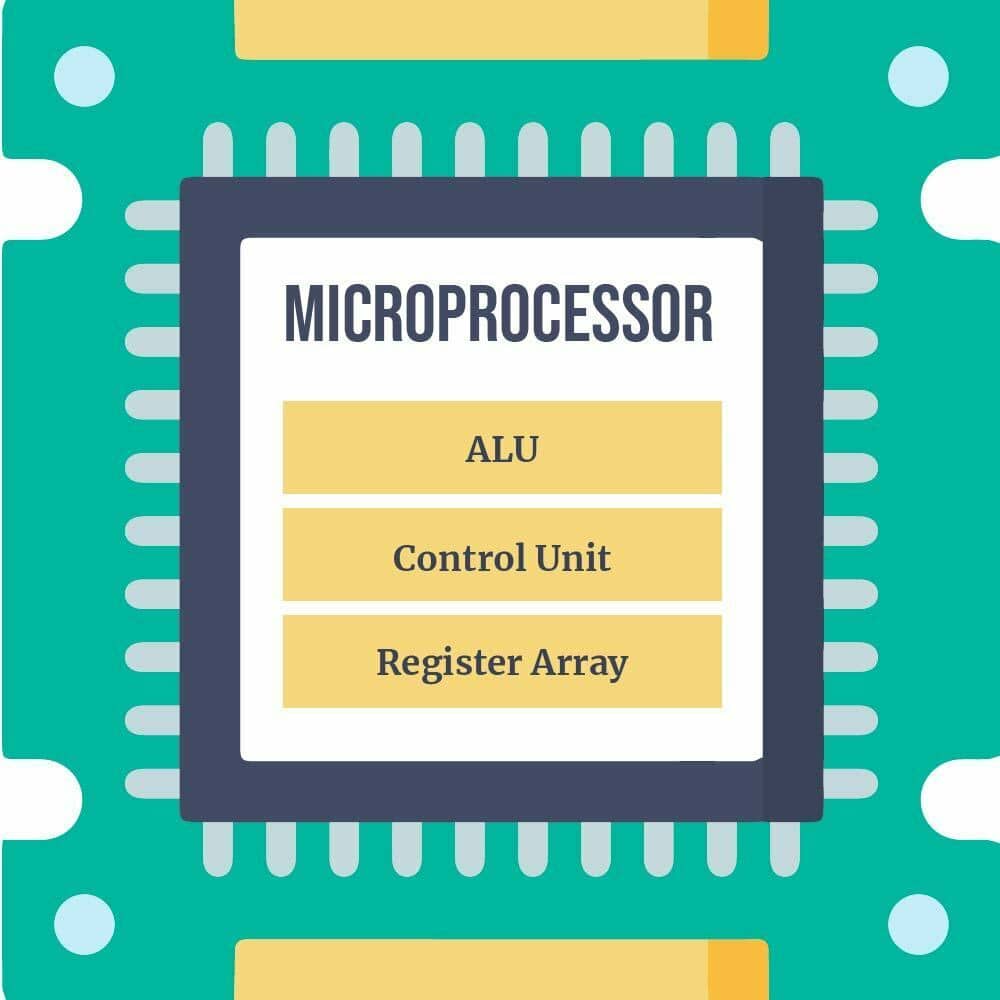
A microprocessor (sometimes called an MPU or Microprocessor Unit) is a controlling unit of a micro-computer, fabricated on a small chip capable of performing ALU (Arithmetic and Logical Unit) and communicating with the other devices connected to it.
Its utility ranges a vast space from controlling elevators to searching the web. We are very aware that instructions describe everything that a computer does, and these instructions are carried out by? Guess who? The one we are talking about—the Microprocessor.
Microprocessors are not made for a specific task. They are helpful where tasks are complex and tricky, like the development of software, games, and other applications that require high Memory and where input and output are not characterized.
According to Precedence Research, A compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8% is predicted for the global microprocessor market, which was valued at USD 106 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 185.39 billion by 2032.
This growth can be attributed to the expanding use of embedded microprocessors in the healthcare electronics industry as well as the growing use of microprocessors in smartphones.

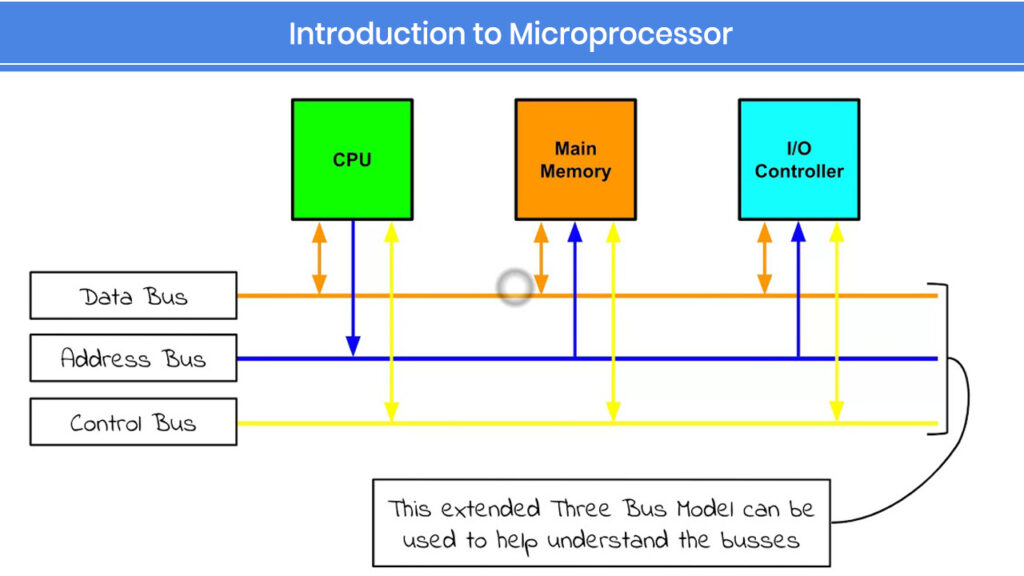
The below given are buses in microprocessor:
System Bus:
A bus is a collection of wires or lines used to send and receive data (bits) between computer components. They are essentially channels of communication that transfer signals between peripherals and microprocessors.
The system bus of a microprocessor is of three types :
Address Bus:
- It is a group of lines that send a memory address or a device address from the Microprocessor Unit (MPU) to the memory or the peripheral.
- The address bus is always unidirectional i.e. address always goes out of the microprocessor.
- If the address line is ‘n’ for an MPU then its addressing capacity is 2n.
Data Bus:
- It is a group of lines used to transfer data between the microprocessor and peripherals and/or memory.
- The data bus is always bi-directional.
Control Bus:
- The control bus in the microprocessor provides signals to control the flow of data.
The computer system’s microprocessor is referred to as its heart. It is an integrated circuit that functions as a central processing unit, or CPU, and can be simple or singular at times.
They contain circuitry for logic, arithmetic, and control. With digital computers, they can accomplish a variety of tasks.
Microprocessors were a component of the microcomputer design. Computers’ use of microprocessors made it possible to microprocess a wide range of commercial, scientific, and industrial tasks.
The following is a list of the different kinds of microprocessors examples:
- CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer): Example: Intel 386, Pentium II, Pentium, Pentium Pro, Intel 486, etc.
- RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer): Example: DEC Alpha 21164, IBM RS6000, DEC Alpha 21064, etc.
- EPIC (Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing): Example: Intel Architecture-64, etc.
Block Diagram – Micro-processor
What is a microcontroller?

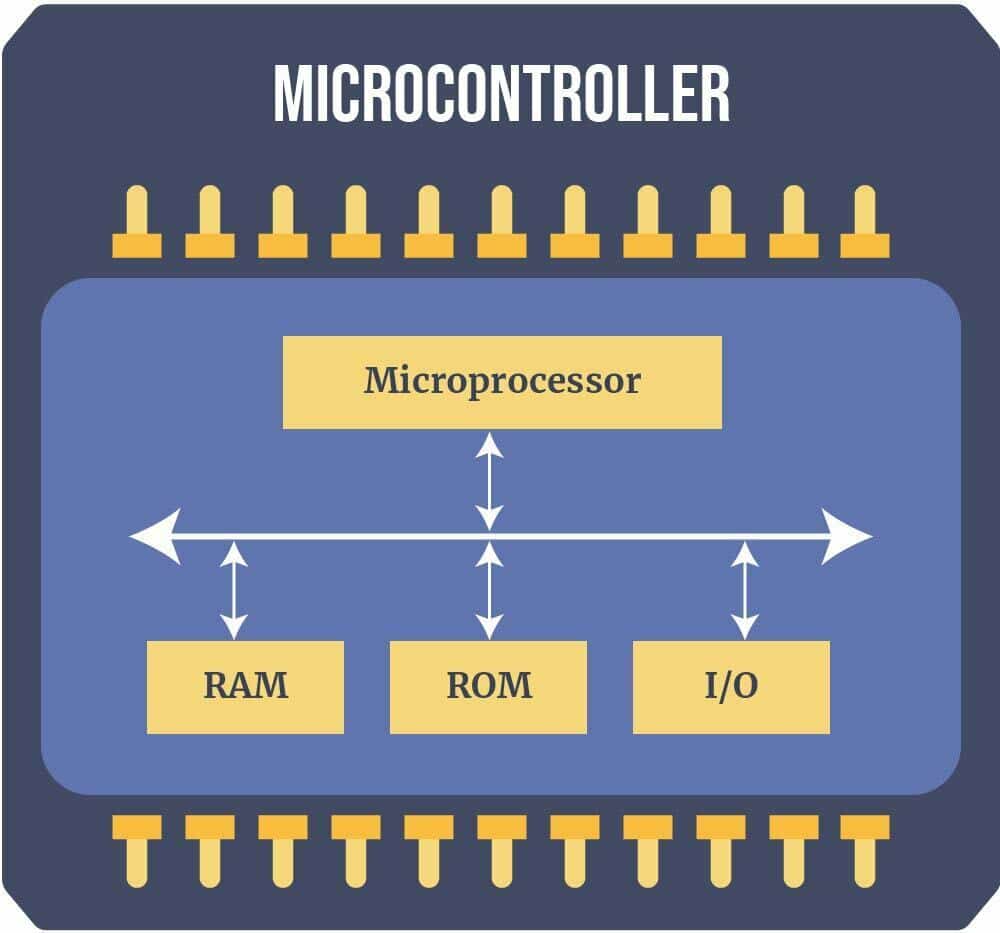
A microcontroller (sometimes called an MCU or Microcontroller Unit) is a single Integrated Circuit (IC) typically utilized for a particular application and designed to execute specific tasks over and over.
It basically contains Memory, processor, and programmable I/O. Essentially, a microcontroller gathers input, processes this information, and outputs a specific action based on the data collected.
Products and gadgets that should be automatically controlled in certain situations, like appliances, power tools, automobile engine control systems, and computers, are some of the microcontroller examples.
According to Precedence Research, The value of the global microcontroller (MCU) market was estimated at USD 27 billion in 2022, and it is projected to increase at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.9% from 2023 to 2032, reaching USD 69.08 billion.

Elements of Microcontroller:
Microcontroller processor (CPU) — Consider a CPU to be the device’s brain. It interprets and reacts to different commands that control the microcontroller’s operation. This calls for the execution of fundamental logic, I/O, and arithmetic operations. To send commands to other parts of the broader embedded system, it also carries out data transfer activities.
Memory — The information that the processor receives and uses to execute instructions that it has been designed to carry out is stored in a microcontroller’s memory. Two primary forms of memory exist in microcontrollers:
- Long-term data regarding the commands that the CPU executes is kept in program memory. Non-volatile memory, or program memory, retains data over time without requiring a power source.
- Temporary data storage during the execution of instructions requires data memory. Volatile data memory only retains its contents while the device is powered on, making the information it contains transient.
I/O peripherals — The processor’s interface to the outside world is provided by the input and output devices. Information is received by the input ports and sent as binary data to the CPU.
After receiving that data, the processor instructs output devices—which carry out operations outside of the microcontroller by sending them the instructions they need to follow.
Although the processor, memory, and I/O peripherals are the essential components of a microprocessor, other components are often incorporated as well.
Simply put, I/O peripherals are supporting parts that communicate with the processor and memory. Peripherals are any number of supporting parts that fall under this category.
Because they are the means via which the processor is applied, some form of I/O peripheral is essential to a microprocessor.
Block Diagram – Microcontroller
History of microprocessor

- 1st Generation: This was the history of microprocessors between 1971 and 1973. The first 4004 microprocessor, manufactured by INTEL in 1971, had a clock speed of 740 kHz. The other microprocessors on the market at the time, such as National Semiconductor’s IMP-16, Rockwell International PPS-4, and Intell-808, were in use. However, none of these processors were compatible with TTL.
- 2nd Generation: During the years 1973–1978, some of the most well-known 8-bit microprocessors, including the Motorola 6800 and 6801, INTEL–8085, and Zilog’s Z80, were implemented. Because they relied on the fabrication of NMOS technology, they were expensive due to their extremely fast speed.
- 3rd Generation: Using HMOS technology, 16-bit processors were developed and designed during this time. INTEL 8086/80186/80286 and Motorola 68000 and 68010 were developed between 1979 and 1980. Those processors outperformed the 2nd generation processors by a factor of four.
- 4th Generation: This generation used HCMOS fabrication to create 32-bit microprocessors between 1981 and 1995. The most widely used CPUs were Motorola’s 68020 and 68030 and Intel’s 80386.
- 5th Generation: Microprocessor Evolution (1995-Present): In the mid-’90s, fifth-generation microprocessors introduced decoupled superscalar processing. By surpassing 10 million transistors, PCs became a high-volume, low-margin business with a single dominant microprocessor. The early 2000s saw the advent of 64-bit microprocessors, such as AMD’s x86-64 and Intel’s compatible extensions, ushering in the desktop era.
- Intel’s Pentium, Celeron, and dual-core processors, along with AMD’s innovations, achieved speeds of up to 3.5GHz. The move to 64 bits significantly expanded register size and doubled the number of general-purpose registers. PowerPC processors smoothly transitioned to 64 bits.
- 2011 – Till Date: ARM introduced a new 64-bit architecture. The latest developments include the introduction of dual-core processors by both Intel and AMD, enabling a single processor to handle the work of two. This evolution reflects a continuous focus on on-chip functionalities, memory, and I/O speed improvements.
Thus, the microprocessor has evolved through all these generations, and the fifth-generation microprocessors represent an advancement in specifications.
History of micro-controller
Here are some fundamental milestones in the evolution of microcontrollers:
- Intel invented the first micro-controller named Intel 8048 in 1975
- The introduction of EEPROM happened in 1993
- That very year, Atmel presented the first Microcontroller utilizing Flash memory.
Types of Microprocessors:
Microprocessor vs Microcontroller: Microprocessors are classified into five types-
#1. CISM – Complex Instruction Set Microprocessors:
CISM or Complex Instruction Set type is equipped for executing single instructions using several low-level functions. Several operations like load from Memory, store in Memory, or arithmetic operations can be performed using these low-level functions. Also, it can likewise perform complex computations.
#2. RISM – Reduced Instruction Set Microprocessors:
While working with fewer instructions than CISM, one can utilize RISM or Reduced Instruction Set type. It is comprised of a set of simple instructions and is also optimized for regular instruction pipeline flow. RISM is the most commonly used processor.
#3. ASIC – Application-Specific Integrated Circuits:
This type of integrated circuit is used for explicit purposes only. They can be used in a digital voice recorder or a bitcoin miner. The design is highly modern, and they may include the entire Microprocessor in a single chip.
Microprocessor Vs Integrated circuits: Microprocessor vs. Integrated Circuit: A computer’s microprocessor, which runs programs by carrying out calculations and executing instructions, is its brain.
It condenses the central processor unit (CPU) functions of a computer onto a single chip. Conversely, an integrated circuit (IC) is a more general word for a collection of electronic circuits on a compact, flat piece of semiconductor material, most often silicon.
Microprocessors are one type of integrated circuit (IC), along with memory chips, logic chips, and other specialized parts. In essence, integrated circuits are microprocessors, although not all microprocessors are integrated circuits.
#4. DSPs – Digital Signal Processors:
Digital Signal Processor requires several components like the term memory, input/output, and program memory. We can use this processor to process analog signals to digital signals and vice-versa. It is also used for encoding and decoding videos.
#5. Superscalar Processors:
Superscalar Processor is capable of implementing instruction-level parallelism and that too within a single processor. It can execute more than one instruction per clock cycle. As a result, this kind of processor is quick and gives more throughput than primitive scalar processors.
Types of Micro-controller
Microcontrollers are classified into various categories based on Memory, bits, and instruction sets. Following is the rundown of their types −
Bit
In light of bit configuration, the Microcontroller is additionally divided into three categories.
- 8-bit Microcontroller − This type of Microcontroller executes arithmetic and logical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication division, etc. For instance, Intel 8031 and 8051 are 8 bits microcontrollers.
- 16-bit Microcontroller − This type of Microcontroller is used to perform arithmetic and logical operations where higher accuracy and performance are required. For example, Intel 8096 is a 16-bit microcontroller.
- 32-bit Microcontroller − This type of Microcontroller is generally used in automatically controlled appliances like automatic operational machines, medical devices, etc.
Memory
In light of the memory configuration, the Microcontroller is additionally divided into two categories.
- External memory microcontroller − This type of Microcontroller is designed such that they do not have a program memory on the chip. Hence, it is named as external memory microcontroller. For example- Intel 8031 microcontroller.
- Embedded memory microcontroller − This type of Microcontroller is designed so that the Microcontroller has all programs and data memory, counters, and timers, interrupts, I/O ports embedded on the chip. For example- Intel 8051 microcontroller.
Instruction Set
In light of the instruction set configuration, the Microcontroller is additionally divided into two categories.
- CISC − CISC stands for complex instruction set computer. It allows the user to insert a single instruction as an alternative to many simple instructions.
- RISC − RISC stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computers. It reduces the operational time by shortening the clock cycle per instruction.
Features of Microprocessor
Microprocessor vs Microcontroller: Here is a list of some of the prominent features-
- Diversity- Microprocessors have a high computational capacity with no storage constraints. Also, it offers a built-in monitor/debugger program with interrupt capability.
- Versatility − The microprocessors can be used for various purposes by configuring the software program, so it is considered versatile.
- Reliability −As the microprocessors use semiconductor technology, so the chances of failure are significantly less. Hence, the microprocessors are very reliable.
- High Speed – A microprocessor can execute millions of instructions per second. As a result, they can work at a very high speed.
Features of micro-controller
Microprocessor vs Microcontroller: Here is a list of some of the prominent features-
- Small Size: A microcontroller is more compact in size.
- Efficiency: A microcontroller is more efficient because of its compact size.
- Clock speed: The clock speed of the Microcontroller is less as compared to a microprocessor.
- Structure: The structure of a microcontroller is fixed.
- Power Consumption: The power consumption for the Microcontroller is less. It also offers Power saving mode.
Microprocessor vs Microcontroller:
Each of the two microcontrollers and microprocessors has special advantages suited for particular uses.
In the context of microcontroller vs microprocessor comparison, microcontrollers are particularly noteworthy for their cost-effectiveness, low power consumption, and integrated peripherals, which make them perfect for embedded systems and battery-powered devices.
However, microprocessors are superior in terms of processing capacity and adaptability, making them appropriate for high-performance activities and intricate calculations in servers and PCs.
In situations when cost, efficiency, and integration are the advantages of microcontrollers over microprocessors.
Everything you need to know about microcontrollers and microprocessors is explained in the comparison below.
Applications of Microprocessor
Microprocessors are extensively utilized in many different industries for a wide range of applications. Among the typical applications of microprocessors are
Consumer Electronics: Many consumer electronics, such as smartphones, TVs, digital cameras, video game consoles, and home appliances like washing machines, refrigerators, and microwaves, use microprocessors.
Automotive: Automotive microprocessors are used to regulate the engine, transmission, and braking systems, among other systems. They also offer infotainment systems, GPS, and driver assistance systems, among other features.
Medical: Medical devices that monitor and regulate a patient’s health, like blood glucose meters, insulin pumps, and pacemakers, use microprocessors.
Industrial Control Systems: PLCs, robotics, and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are examples of industrial control systems that use microprocessors to monitor and control a variety of processes.
Aerospace and Defense: Avionics, radar, and missile guidance systems are just a few of the defense and aerospace systems that use microprocessors.
Communication: Microprocessors are used to process and transmit data in communication systems like switches, routers, and modems.
Security: Microprocessors are used to process and store data in security systems like surveillance cameras and access control systems.
Education: Microprocessors are utilized in educational kits and toys to instruct kids in electronics and programming.
Entertainment: To create immersive gaming experiences, virtual reality systems and gaming consoles use microprocessors.
Applications of microcontroller

Numerous devices, such as automated systems, sensing and monitoring equipment, and machine control, employ microcontrollers. Typical applications of microcontrollers include the following:
Industrial automation: Industrial devices like robotic arms, conveyor belts, and other machinery used in manufacturing are frequently controlled by microcontrollers.
Automotive: In cars, microcontrollers are used to operate the engine, transmission, and brakes, among other systems.
Home appliances: Microcontrollers are used in many home appliances, including refrigerators, microwaves, and washing machines, to regulate their various operations.
Consumer electronics: Numerous consumer electronics, such as tablets, smartphones, and other portable devices, use microcontrollers.
Medical devices: Insulin pumps, blood pressure monitors, heart rate monitors, and other medical devices all use microcontrollers.
Military systems: Military systems like missiles, airplanes, and other defense systems use microcontrollers.
Environmental monitoring: Sensors and other equipment that keep an eye on environmental factors like humidity, temperature, and air quality use microcontrollers.
Robotics: Robots use microcontrollers to regulate their motion and carry out a variety of functions.
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices use microcontrollers to perform a variety of functions as well as data collection and transmission.
In the End:
If you have come this far, you would have probably understood that both microprocessors and microcontrollers are meant to serve vastly different types of applications.
It is basically different ways of organizing and optimizing a computer system based on a CPU. Microprocessors, which houses a more powerful CPU on a single chip and connect to external peripherals, are meant for applications like graphic control, motherboard, or intense-data processing systems because of their high processing power and versatile computing operations.
Microprocessor vs Microcontroller: which put the CPU and all peripherals onto the same chip, are used to target compact, specific, low-power applications like music players, drones, or robotic applications.
Regardless of choice, both microprocessors and microcontrollers have their design challenges. Microprocessors usually have large pin counts, with many of them forming the system bus; hence there is a need to ensure the data and address bus are routed in equal length to prevent timing issues.
If a Microcontroller is used, there is a concern about the operating reliability of mixed signals on a compact PCB, ensuring signal integrity for analog channels while ensuring the digital signals are not coupling noises to adjacent components Microprocessor vs Microcontroller.
Some Commonly asked Questions:
Q: Which is better, a Microprocessor or a Microcontroller?
The decision between a microprocessor and a microcontroller ultimately comes down to the particular application requirements, which may include processing capacity, system complexity, power consumption, cost, flexibility, and development considerations. To determine the best microcontroller or microprocessor for the project, it is imperative to meticulously consider these factors.
Q: Is Raspberry Pi a Microcontroller or Microprocessor?
The Raspberry Pi is a microprocessor-based single-board computer.
Q: Is Arduino a Microcontroller or a Microprocessor?
Arduino is a microcontroller-based development board.
Q: Does every Microcontroller have a Microprocessor?
Indeed, the central component of every microcontroller is a microprocessor. Within the microcontroller, the microprocessor is in charge of carrying out calculations and executing instructions. It’s crucial to remember that while microprocessors are a component of all microcontrollers, not all microcontrollers have microprocessors. Microprocessors can also be used as independent parts in different kinds of applications.
Q: What are the Different Applications for Microprocessors and Microcontrollers?
Microprocessor use cases:
- Personal computers
- Servers
- Mobile devices
- Gaming consoles
- High-performance computing
Microcontroller use cases:
- Embedded systems
- Automotive microcontroller systems
- Consumer electronics
- Medical devices
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
Q: What is FPGA vs. microcontroller? When to use FPGA in a microcontroller?
Microcontrollers are designed for sequential processing, but FPGAs are superior at applications requiring parallel processing.
Because of their parallel architecture, which comprises several reconfigurable logic blocks and interconnects, FPGAs may perform multiple operations at once.
It’s important to take into account the kind of jobs that FPGAs and microcontrollers are intended to do when comparing their respective performances.
Microcontrollers are designed for sequential processing, but FPGAs are superior at applications requiring parallel processing.
Q: What is the difference between 32-bit and 16-bit microcontrollers?
A 32-bit address bus on 32-bit microcontrollers allows access to up to 4 gigabytes (Gbytes) of memory. The 16 bits of addressing on conventional 16-bit microcontrollers can only access 64 kilobytes (Kbytes).
Q: What is a PIC microcontroller
The General Instruments Microcontrollers invented the PIC microcontroller, or peripheral interface microcontroller, in 1993. It is programmed to carry out various functions and manage a generation line through software control.
Q: What is a single-board computer Vs a microcontroller
All that a microcontroller is is the SBC’s processor. A microcontroller can have 64 bits and 80 pins or more, or it can have 8 bits and only 6 pins. ARM core is used by SBCs like Raspberry Pi.
SBCs include integrated interface chipsets and additional hardware for communication, whereas microcontrollers require these components externally on PCBs.
I guess every brief aspect, be their applicability or structure, I have covered it all, well and good. Nevertheless, if you still have any questions, send them our way. You can reach out to us at info@logic-fruit.com.







